回溯Backtracking Algorithm
回溯Backtracking Algorithm
1) 入门例子
1 | /** |
如果是集合又有什么样的效果呢?
1 | 如果用的是可变的集合或者数组必须手动的恢复集合状态 |
1 | public class Backtracking { |
1 | rec(1, []) |
1 | before:[] |
这段代码虽然简单,但完整地展示了回溯的三步:
选择 → 递归 → 撤销,最终输出是:
2) 全排列-Leetcode 46
给定一个不含重复数字的数组 nums ,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
1 | 输入:nums = [1,2,3] |
示例 2:
1 | 输入:nums = [0,1] |
示例 3:
1 | 输入:nums = [1] |
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 6-10 <= nums[i] <= 10nums中的所有整数 互不相同
1 | [] |
1 | public class PermuteLeetcode46 { |
3) 全排列II-Leetcode 47
给定一个可包含重复数字的序列 nums ,按任意顺序 返回所有不重复的全排列。
示例 1:
1 | 输入:nums = [1,1,2] |
示例 2:
1 | 输入:nums = [1,2,3] |
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 8-10 <= nums[i] <= 10
1 | [] |
- 根节点:
[]表示空排列,即还没有选择任何数字。- 第一层:从根节点开始,我们有两个选择:
1和3。这是因为数组中有两个不同的数字。- 第二层:
- 选择
1后,我们再次面临选择:1'(表示另一个1)和3。- 选择
3后,我们只有选择1和1'。- 第三层:
- 从
1和1',我们可以得到排列11'3和131'。- 从
3和1,我们可以得到排列31和311'。- 叶节点:这些叶节点表示完整的排列,如
11'3,131',31,311'。避免重复排列:
- 在选择下一个数字时,我们使用了一个技巧来避免重复。例如,当我们已经选择了
1,我们不会再次选择1,直到我们已经选择了3。这样可以确保每个排列都是唯一的。- 在代码实现中,这通常通过在递归调用前检查当前数字是否已经被选择来实现。
1 | public class PermuteLeetcode47 { |
排好序,这样重复的数字会相邻
定好规则:必须 1 固定之后才能固定 1’,即 1 的 visited = true 才能继续处理 1’
在遍历时,遇到了 nums[i] == nums[i - 1](即 1 和 1‘ 这种情况),进一步检查 i-1 位置的数字有没有 visited,没有,则不处理(剪枝)
也可以看我CSDN博客
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_79602614/article/details/138347128
4) 组合-Leetcode 77
给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回范围 [1, n] 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。
你可以按 任何顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
1 | 输入:n = 4, k = 2 |
示例 2:
1 | 输入:n = 1, k = 1 |
提示:
1 <= n <= 201 <= k <= n
1 | class Solution { |
dfs(i+1,n,k,stack,result); 如果改为:dfs(1,n,k,stack,result);
改为:dfs(i,n,k,stack,result); 情况都不同 可以自行体悟一下
减枝
如果缺的数字大于备用数字 那么就要剪枝剪掉
k- stack.length 还差几个能凑满
n - i +1 还剩下几个备用数字 if(k-stack.length >n-i+1) continue;
1 | class Solution { |
1 | public class CombinationLeetcode77 { |
k 代表剩余要组合的个数
n - i + 1 代表剩余可用数字
剪枝条件是:剩余可用数字要大于剩余组合数
为啥放在外面不行?即这行代码:if (k > n - start + 1) { return; }
因为它只考虑了 start 一种情况,而实际在循环内要处理的是 start,start+1 … n 这多种情况
似乎 ArrayList 作为 stack 性能高一些,见下面代码,但是这道题在 leetcode 上执行时间不稳定,相同代码都会有较大时间差异(15ms vs 9ms)
1 | class Solution { |
5) 组合总和-Leetcode 39
1 | class Solution { |
与之前的零钱兑换问题其实是一样的,只是
- 本题求的是:所有组合的具体信息
- 零钱兑换问题求的是:所有组合中数字最少的、所有组合个数… [动态规划]
6) 组合总和 II-Leetcode 40
给定一个候选人编号的集合 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用 一次 。
**注意:**解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
1 | 输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8, |
示例 2:
1 | 输入: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5, |
提示:
1 <= candidates.length <= 1001 <= candidates[i] <= 501 <= target <= 30
1 | public class CombinationLeetcode40 { |
7) 组合总和 III-Leetcode 216
找出所有相加之和为 n 的 k 个数的组合,且满足下列条件:
- 只使用数字1到9
- 每个数字 最多使用一次
返回 所有可能的有效组合的列表 。该列表不能包含相同的组合两次,组合可以以任何顺序返回。
示例 1:
1 | 输入: k = 3, n = 7 |
示例 2:
1 | 输入: k = 3, n = 9 |
示例 3:
1 | 输入: k = 4, n = 1 |
提示:
2 <= k <= 91 <= n <= 60
1 | class Solution { |
8) N 皇后Leetcode 51
Eight queens 高斯认为有76种方案。实际上解有92种。
按照国际象棋的规则,皇后可以攻击与之处在同一行或同一列或同一斜线上的棋子。
n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
给你一个整数 n ,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题 的解决方案。
每一种解法包含一个不同的 n 皇后问题 的棋子放置方案,该方案中 'Q' 和 '.' 分别代表了皇后和空位。
示例 1:
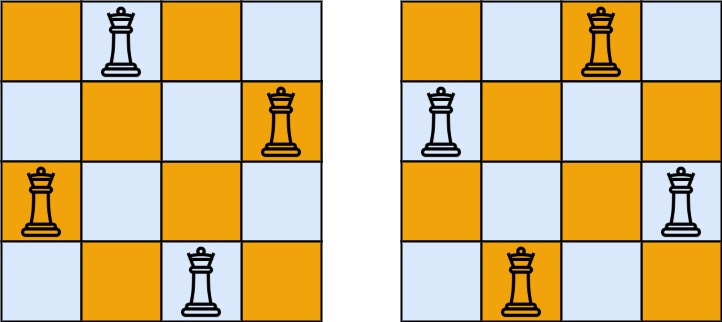
1 | 输入:n = 4 |
示例 2:
1 | 输入:n = 1 |
提示:
1 <= n <= 9
左斜线处理i+j
右斜线i-j = n-1-(i-j)
1 | public class NQueenLeetcode51 { |
1 | public class NQueenLeetcode51 { |
9) 解数独-Leetcode37
编写一个程序,通过填充空格来解决数独问题。
数独的解法需 遵循如下规则:
- 数字
1-9在每一行只能出现一次。 - 数字
1-9在每一列只能出现一次。 - 数字
1-9在每一个以粗实线分隔的3x3宫内只能出现一次。(请参考示例图)
数独部分空格内已填入了数字,空白格用 '.' 表示。
示例 1:
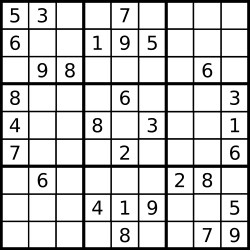
1 | 输入:board = [["5","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."],["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."],[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."],["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"],["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"],["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"],[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."],[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"],[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]] |
提示:
board.length == 9board[i].length == 9board[i][j]是一位数字或者'.'- 题目数据 保证 输入数独仅有一个解
判断在那个九宫格 ==> i/3*3+j/3
1 | public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) { |
1 | public class SudokuLeetcode37 { |
1 | public class SudokuLeetcode37 { |
10) 黄金矿工-Leetcode1219
你要开发一座金矿,地质勘测学家已经探明了这座金矿中的资源分布,并用大小为 m * n 的网格 grid 进行了标注。每个单元格中的整数就表示这一单元格中的黄金数量;如果该单元格是空的,那么就是 0。
为了使收益最大化,矿工需要按以下规则来开采黄金:
- 每当矿工进入一个单元,就会收集该单元格中的所有黄金。
- 矿工每次可以从当前位置向上下左右四个方向走。
- 每个单元格只能被开采(进入)一次。
- 不得开采(进入)黄金数目为
0的单元格。 - 矿工可以从网格中 任意一个 有黄金的单元格出发或者是停止。
示例 1:
1 | 输入:grid = [[0,6,0],[5,8,7],[0,9,0]] |
示例 2:
1 | 输入:grid = [[1,0,7],[2,0,6],[3,4,5],[0,3,0],[9,0,20]] |
提示:
1 <= grid.length, grid[i].length <= 150 <= grid[i][j] <= 100- 最多 25 个单元格中有黄金。
1 | class Solution { |
LeetCode 543
给你一棵二叉树的根节点,返回该树的 直径 。
二叉树的 直径 是指树中任意两个节点之间最长路径的 长度 。这条路径可能经过也可能不经过根节点 root 。
两节点之间路径的 长度 由它们之间边数表示。
示例 1:

1 | 输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5] |
示例 2:
1 | 输入:root = [1,2] |
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[1, 104]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
1 | class Solution { |
LeetCode433
基因序列可以表示为一条由 8 个字符组成的字符串,其中每个字符都是 'A'、'C'、'G' 和 'T' 之一。
假设我们需要调查从基因序列 start 变为 end 所发生的基因变化。一次基因变化就意味着这个基因序列中的一个字符发生了变化。
- 例如,
"AACCGGTT" --> "AACCGGTA"就是一次基因变化。
另有一个基因库 bank 记录了所有有效的基因变化,只有基因库中的基因才是有效的基因序列。(变化后的基因必须位于基因库 bank 中)
给你两个基因序列 start 和 end ,以及一个基因库 bank ,请你找出并返回能够使 start 变化为 end 所需的最少变化次数。如果无法完成此基因变化,返回 -1 。
注意:起始基因序列 start 默认是有效的,但是它并不一定会出现在基因库中。
示例 1:
1 | 输入:start = "AACCGGTT", end = "AACCGGTA", bank = ["AACCGGTA"] |
示例 2:
1 | 输入:start = "AACCGGTT", end = "AAACGGTA", bank = ["AACCGGTA","AACCGCTA","AAACGGTA"] |
示例 3:
1 | 输入:start = "AAAAACCC", end = "AACCCCCC", bank = ["AAAACCCC","AAACCCCC","AACCCCCC"] |
提示:
start.length == 8end.length == 80 <= bank.length <= 10bank[i].length == 8start、end和bank[i]仅由字符['A', 'C', 'G', 'T']组成
这道题目是一个典型的最短路径问题,但是它在基因序列的背景下进行。题目要求我们找到从基因序列
start变化到end的最少变化次数。这里的“变化”指的是基因序列中的一个字符发生了变化。题目中还提供了一个基因库bank,只有基因库中的基因序列才是有效的,即变化后的基因序列必须出现在基因库中。题目详解
- 基因序列:由8个字符组成,每个字符可以是 ‘A’、‘C’、‘G’ 或 ‘T’。
- 基因变化:指的是基因序列中的一个字符发生了变化,例如 “AACCGGTT” 变为 “AACCGGTA”。
- 基因库
bank:记录了所有有效的基因变化,只有出现在bank中的基因序列才是有效的。- 目标:找到从
start变化到end所需的最少变化次数。如果无法完成变化,返回 -1。- 输入:
start:起始基因序列。end:目标基因序列。bank:有效的基因序列列表。- 输出:最少变化次数,如果无法完成变化,则返回 -1。
示例解释
- 示例 1:从 “AACCGGTT” 到 “AACCGGTA” 只需要一次变化,因为 “AACCGGTA” 在基因库中。
- 示例 2:从 “AACCGGTT” 到 “AAACGGTA” 需要两次变化,可能的路径是 “AACCGGTT” → “AACCGCTA” → “AAACGGTA”,这两个中间基因序列都在基因库中。
- 示例 3:从 “AAAAACCC” 到 “AACCCCCC” 需要三次变化,可能的路径是 “AAAAACCC” → “AAAACCCC” → “AAACCCCC” → “AACCCCCC”,这三个中间基因序列都在基因库中。
解题思路
题目中提供的代码使用了回溯法来解决这个问题。以下是代码的逻辑解释:
- 初始化:
ans用于存储最少变化次数,初始值为Integer.MAX_VALUE。- 递归函数
backtrack:
- 参数
start:当前基因序列。- 参数
end:目标基因序列。- 参数
bank:基因库。- 参数
used:一个布尔数组,用于标记基因库中的哪些基因序列已经被使用过。- 参数
t:当前的变化次数。- 递归终止条件:
- 如果当前变化次数
t已经大于等于ans,则直接返回,因为不可能找到更短的路径。- 如果当前基因序列
start等于目标基因序列end,则更新ans为当前的最小变化次数。- 递归搜索:
- 遍历基因库
bank,对于每个基因序列,检查它是否与当前基因序列start只有一个字符不同(即变化次数为1)。- 如果找到这样的基因序列,标记为已使用,递归调用
backtrack函数,尝试找到从这个基因序列变化到end的最少变化次数。- 递归完成后,取消标记(回溯),以便其他路径可以使用这个基因序列。
- 返回结果:
- 如果
ans仍然是Integer.MAX_VALUE,说明无法从start变化到end,返回 -1。- 否则,返回
ans。
1 | class Solution { |
代码解释
diff的作用:diff用于计算当前基因序列start和基因库中的某个基因序列bank[i]之间的差异。- 具体来说,
diff计算的是两个序列中对应位置上不同字符的个数。 - 如果
diff等于 1,表示两个序列之间只有一个字符不同,即可以通过一次变化从start变为bank[i]。
bank的使用:bank是一个数组,包含了所有有效的基因序列。- 在回溯过程中,我们遍历
bank中的每个基因序列,检查它是否可以作为从start到end的一个中间步骤。 - 只有当
bank[i]与start的差异为 1 时,bank[i]才会被考虑作为下一步。
举例说明
假设我们有以下输入:
start = "AACCGGTT"end = "AAACGGTA"bank = ["AACCGGTA", "AACCGCTA", "AAACGGTA"]
步骤 1:初始化
ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE(初始的最少变化次数设为最大整数值)
步骤 2:第一次调用 backtrack
backtrack("AACCGGTT", "AAACGGTA", bank, new boolean[bank.length], 0)
步骤 3:遍历 bank
- 计算
start和每个bank[i]的差异diff:diff("AACCGGTT", "AACCGGTA") = 2(两个字符不同)diff("AACCGGTT", "AACCGCTA") = 1(一个字符不同)diff("AACCGGTT", "AAACGGTA") = 2(两个字符不同)
- 只有
"AACCGCTA"的diff为 1,因此我们选择它作为下一步。
步骤 4:递归调用 backtrack
used[1] = true(标记 “AACCGCTA” 为已使用)backtrack("AACCGCTA", "AAACGGTA", bank, used, 1)
步骤 5:再次遍历 bank
- 计算
"AACCGCTA"和每个bank[i]的差异diff:diff("AACCGCTA", "AACCGGTA") = 2diff("AACCGCTA", "AAACGGTA") = 1
- 只有
"AAACGGTA"的diff为 1,因此我们选择它作为下一步。
步骤 6:再次递归调用 backtrack
used[2] = true(标记 “AAACGGTA” 为已使用)backtrack("AAACGGTA", "AAACGGTA", bank, used, 2)
步骤 7:达到目标
start.equals(end)为true,更新ans = 2
步骤 8:回溯
- 取消标记
used[2] = false,used[1] = false - 返回到上一级递归
最终,我们找到了从 "AACCGGTT" 到 "AAACGGTA" 的最少变化次数为 2。
总结
通过这个例子,我们可以看到 diff 是如何计算两个序列之间的差异,并且 bank 是如何被用来找到有效的中间步骤。代码通过递归和回溯,尝试所有可能的路径,直到找到最短的路径或确定不存在这样的路径。





